- Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Javatpoint
- Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Geeksforgeeks
- Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering 6th Edition
- Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Software
Effort Estimation In Software Engineering Such function can be determined from data from completed projects using statistical techniques like fitting a regression curve through the scatter plot obtained by plotting the effort. Hybrid software process simulation models combining discrete event and system dynamics approaches are also introduced to support software project estimation and project management. 32 formalize communication overhead and use a search-based project staffing and scheduling approach on two large real world maintenance projects.
- Estimation Techniques Tutorial
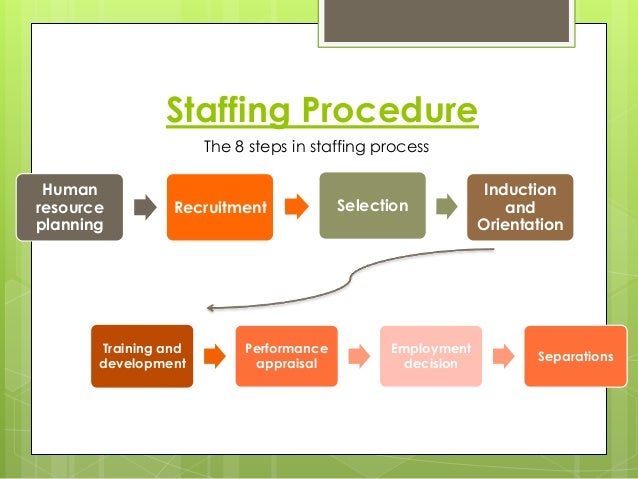
Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Professional Organizations Of These estimates are needed before development is initiated, as they establish the cost and schedule goals of the project. The managers estimate efforts in terms of personnel requirement and man-hour required to produce the software. For effort estimation software size should be known. This can either be derived by managers’ experience, organization’s historical data or software size can be converted into efforts by using some standard formulae. Time estimation. Estimation of the size of software is an essential part of Software Project Management. It helps the project manager to further predict the effort and time which will be needed to build the project. Various measures are used in project size estimation. Some of these are.
- Estimation Techniques Resources
- Selected Reading
Project Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT) estimation considers three values: the most optimistic estimate (O), a most likely estimate (M), and a pessimistic estimate (least likely estimate (L)). There has been some confusion regarding Three-point Estimation and PERT in the Industry. However, the techniques are different. You will see the differences as you learn the two techniques. Also, at the end of this chapter, the differences are collated and presented.
PERT is based on three values − most optimistic estimate (O), a most likely estimate (M), and a pessimistic estimate (least likely estimate (L)). The most-likely estimate is weighted 4 times more than the other two estimates (optimistic and pessimistic).
Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Javatpoint
PERT Estimate (E) is based on the weighted average and follows beta distribution.
E = (O + 4 × M + L)/6
PERT is frequently used along with Critical Path Method (CPM). CPM tells about the tasks that are critical in the project. If there is a delay in these tasks, the project gets delayed.
Standard Deviation
Standard Deviation (SD) measures the variability or uncertainty in the estimate.
In beta distribution,
Mean = (O + 4 × M + L)/6
Standard Deviation (SD) = (L − O)/6
PERT Estimation Steps
Step (1) − Arrive at the WBS.
Step (2) − For each task, find three values most optimistic estimate (O), a most likely estimate (M), and a pessimistic estimate (L).
Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Geeksforgeeks
Step (3) − PERT Mean = (O + 4 × M + L)/6
PERT Mean = (O + 4 × M + L)/3
Step (4) − Calculate the Standard Deviation of the task.
Standard Deviation (SD) = (L − O)/6
Step (6) − Repeat steps 2, 3, 4 for all the tasks in the WBS.
Step (7) − Calculate the PERT estimate of the project.
E (Project) = ∑ E (Task)
Step (8) − Calculate the Standard Deviation of the project.
SD (Project) = √ (ΣSD (Task)2)
Convert the Project Estimates to Confidence Levels

PERT Estimate (E) and Standard Deviation (SD) thus calculated are used to convert the project estimates to confidence levels.
The conversion is based such that
Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering 6th Edition
- Confidence level in E +/– SD is approximately 68%.
- Confidence level in E value +/– 1.645 × SD is approximately 90%.
- Confidence level in E value +/– 2 × SD is approximately 95%.
- Confidence level in E value +/– 3 × SD is approximately 99.7%.
Commonly, the 95% confidence level, i.e., E Value + 2 × SD, is used for all project and task estimates.
Differences between Three-Point Estimation and PERT
Following are the differences between Three-Point Estimation and PERT −
Staffing Level Estimation In Software Engineering Software
| Three-Point Estimation | PERT |
|---|---|
| Simple average | Weighted average |
| Follows triangular Distribution | Follows beta Distribution |
| Used for small repetitive projects | Used for large non-repetitive projects, usually R&D projects. Used along with Critical Path Method (CPM) |
E = Mean = (O + M + L)/3 This is simple average | E = Mean = (O + 4 × M + L)/6 This is weighted average |
| SD = √ [((O − E)2 + (M − E)2 + (L − E)2)/2] | SD = (L − O)/6 |
